1976 proposed by Peter Chen.
What are the fundamentals required for understanding and designing ER diagrams?
How ER modeling is performed?
The basic concepts involved in ER diagrams are as follows:
Type of Attributes
• Entities with the same basic attributes are grouped or typed into an entity type.
• In ER diagrams, an entity type is displayed in a rectangular box
• Each entity type will have a collection of entities stored in the database
• Based on the requirements, we can identify four initial entity types in the COMPANY database:
• By examining the requirements, six relationship types are identified
• In the refined design, some attributes from the initial entity types are refined into relationships:
• An relationship type whose with the same participating entity type in distinct roles
• An entity that does not have a key attribute
• Constraints on Relationship Types
Displaying a recursive relationship
Attributes of Relationship types
• Cardinality ratio (of a binary relationship): 1:1, 1:N, N:1, or M:N
Objectives
What are ER Model?
What are the fundamentals required for understanding and designing ER diagrams?
How ER modeling is performed?
What are ER Model?
- Entity – Relationship model (ER model) in software engineering is an abstract way to describe a database.
- Relational database, stores data in tables. Some of the data’s(entities) in these tables point to data’s(entities) in other tables. Diagrams created to design these entities and relationships are called entity–relationship diagrams or ER diagrams.
ER diagram is widely used in database design
- Represent conceptual level of a database system
Describe things and their relationships in high level
What are the fundamentals required for understanding and designing ER diagrams?
The basic concepts involved in ER diagrams are as follows:
1) Entities (and their entity types and entity sets): Entities are specific objects or things in the mini-world that are represented in the database.
E.g. the EMPLOYEE John Smith, the Research DEPARTMENT, the ProductX PROJECT etc.
2) Attributes(simple, composite, multivalued):
• Attributes are properties used to describe an entity.
e.g. an EMPLOYEE entity may have the attributes Name, SSN, Address, Sex, BirthDate
• A specific entity will have a value for each of its attributes.
• Each attribute has a value set (or data type) associated with it – e.g. integer, string etc.
3) Relationships(and their relationship types and relationship sets):
• It relates two or more distinct entities with a specific meaning.
E.g. EMPLOYEE John Smith works on the ProductX
• Relationships of the same type are grouped or typed into a relationship type.
e.g. , the WORKS_ON relationship type in which EMPLOYEEs and PROJECTs participate.
• The degree of a relationship type is the number of participating entity types.
e.g. WORKS_ON is a binary relationships
Concepts in details with examples.
Type of Attributes
• Simple
o Each entity has a single atomic value for the attribute. For example, SSN or Sex.
• Composite
o The attribute may be composed of several components. For example:
Address(Apt#, House#, Street, City, State, ZipCode, Country), or
Name(FirstName, MiddleName, LastName).
Composition may form a hierarchy where some components are themselves composite.
• Multi-valued
o An entity may have multiple values for that attribute. For example, Color of a CAR or PreviousDegrees of a STUDENT.
Denoted as {Color} or {PreviousDegrees}.
In general, composite and multi-valued attributes may be nested arbitrarily to any number of levels, although this is rare.
Entity Types and Key Attributes
• Entities with the same basic attributes are grouped or typed into an entity type.
o For example, the entity type EMPLOYEE and PROJECT.
• An attribute of an entity type for which each entity must have a unique value is called a key attribute of the entity type.
o For example, SSN of EMPLOYEE.
• A key attribute may be composite.
o VehicleTagNumber is a key of the CAR entity type with components (Number, State).
• An entity type may have more than one key.
o The CAR entity type may have two keys:
o VehicleIdentificationNumber (popularly called VIN)
o VehicleTagNumber (Number, State), aka license plate number.
• Each key is underlined.
Displaying an Entity type
• In ER diagrams, an entity type is displayed in a rectangular box
• Attributes are displayed in ovals
o Each attribute is connected to its entity type
o Components of a composite attribute are connected to the oval representing the composite attribute
o Each key attribute is underlined
o Multivalued attributes displayed in double ovals
For example a CAR entity can be shown as below:
Entity Set
• Each entity type will have a collection of entities stored in the database
o Called the entity set
• Below example shows three CAR entity instances in the entity set for CAR.
• Same name (CAR) used to refer to both the entity type and the entity set
• Entity set is the current state of the entities of that type that are stored in the database
Case Study: COMPANY Database Schema.
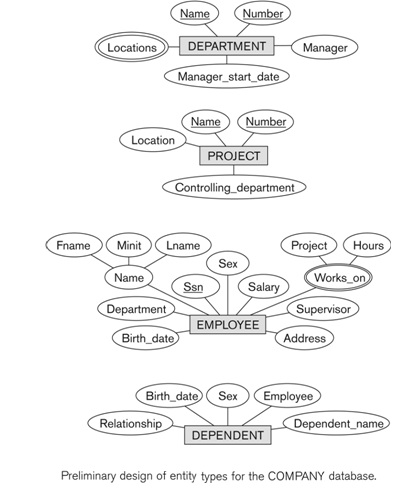
• Based on the requirements, we can identify four initial entity types in the COMPANY database:
o DEPARTMENT
o PROJECT
o EMPLOYEE
o DEPENDENT
Their initial design is shown as below (Note: The initial attributes shown are derived from the requirements description)
Relationship type vs. relationship set
• Relationship Type:
o Is the schema description of a relationship
o Identifies the relationship name and the participating entity types
o Also identifies certain relationship constraints
• Relationship Set:
o The current set of relationship instances represented in the database
o The current state of a relationship type
Relationship instances of the WORKS_FOR N:1 relationship between EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
Relationship instances of the WORKS_FOR M:N relationship between EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
• Previous figures displayed the relationship sets
• Each instance in the set relates individual participating entities – one from each participating entity type
• In ER diagrams, we represent the relationship type as follows:
o Diamond-shaped box is used to display a relationship type
o Connected to the participating entity types via straight lines
o Is the schema description of a relationship
o Identifies the relationship name and the participating entity types
o Also identifies certain relationship constraints
• Relationship Set:
o The current set of relationship instances represented in the database
o The current state of a relationship type
Relationship instances of the WORKS_FOR M:N relationship between EMPLOYEE and DEPARTMENT
• Each instance in the set relates individual participating entities – one from each participating entity type
• In ER diagrams, we represent the relationship type as follows:
o Diamond-shaped box is used to display a relationship type
o Connected to the participating entity types via straight lines










No comments:
Post a Comment